https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1719

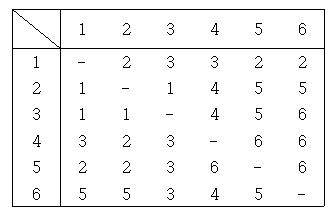
위 그림에서 1번에서 4번으로 가기 위해 최단거리로 이동하는 방법은 3번으로 이동한 후 3번에서 4번으로 이동하는 것이다. 그리고 결과값으로 처음으로 이동한 노드의 번호를 출력하는 것이 문제다.
전체 노드의 개수는 200, 간선의 개수는 10000이므로, 다익스트라알고리즘을 N번한다고 하면 O(N^3) 으로 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
그렇다면 대략적인 알고리즘은 이렇게 될 것이다.
1. 큐에 현재 시작 노드의 이웃 노드들을 집어넣는다.
2. 집어넣을 때 현재 시작 노드를 따로 관리하여 만약 다익스트라 DP가 갱신된다면 첫 입력값을 넣어준다.
오 문제가 해결된 것 같다. 코드로 바꿔보면
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 201
using namespace std;
int answer[MAX][MAX];
int dist[MAX];
int N, M;
vector<pair<int, int>> arr[MAX];
void dijk(int n){
queue<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> q; // 노드번호, 가치, 첫노드번호
for(int i = 0; i < arr[n].size(); i++){
int node = arr[n][i].first;
int value = arr[n][i].second;
int firstNode = node;
dist[node] = value;
answer[n][node] = node;
q.push({node, {value, firstNode}});
}
while(!q.empty()){
int nowNode = q.front().first;
int nowValue = q.front().second.first;
int firstNode = q.front().second.second;
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < arr[nowNode].size(); i++){
int nextNode = arr[nowNode][i].first;
int nextValue = arr[nowNode][i].second;
if(nextNode == n) continue;
if(dist[nextNode] > dist[nowNode] + nextValue){
dist[nextNode] = dist[nowNode] + nextValue;
answer[n][nextNode] = firstNode;
q.push({nextNode,{nextValue, firstNode}});
}
}
}
}
이렇게 될 것이다. 각 큐는 처음시작된 노드를 갖고 있다. 그런데 이렇게 하면 잘못된 결과를 내놓을 수 있다.
왜냐하면 DP배열과 처음 갖고있는 노드는 서로 연관되어 있지 않기 때문이다.
무슨말이냐하면
첫 노드가 1일 때 , DP[3] 을 8로 갱신했다고 하자.
그리고 이후 첫 노드가 2인 놈이 DP[3]에 도착했다. 3과 4가 연결되어 있어서 이쪽으로 이동했다고 하면 첫노드가 1인 놈이니까 그 값을 DP[4] 도 사용해야하는데, DP[3]을 노드 2인놈이 사용했기 때문에 DP값을 마치 다른 노드가 가로챈것이 되어 버린다.
그러므로 큐에 넣어놓지 말고 이전값의 DP값과 더불어 첫노드도 함게 계승받아야 정답이 될 수 있다.
문제 태그에 플로이드워셜도 있어서 다른 방법으로 풀 수도 있는 것 같다.
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 1001
using namespace std;
int answer[MAX][MAX];
int dist[MAX];
int N, M;
vector<pair<int, int>> arr[MAX];
void dijk(int n){
dist[n] = 0;
//cout << "주목 :: " << n << endl;
queue<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> q; // 노드번호, 가치, 첫노드번호
for(int i = 0; i < arr[n].size(); i++){
int node = arr[n][i].first;
int value = arr[n][i].second;
int firstNode = node;
dist[node] = value;
answer[n][node] = firstNode;
q.push({node, {value, firstNode}});
//cout << node << ' ';
}
//cout << endl;
while(!q.empty()){
int nowNode = q.front().first;
int nowValue = q.front().second.first;
int firstNode = q.front().second.second;
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < arr[nowNode].size(); i++){
int nextNode = arr[nowNode][i].first;
int nextValue = arr[nowNode][i].second;
//if(nextNode == n) continue;
if(dist[nextNode] > dist[nowNode] + nextValue){
dist[nextNode] = dist[nowNode] + nextValue;
answer[n][nextNode] = answer[n][nowNode];
// cout << "다음노드 :: " << nextNode << endl;
// cout << "갱신값 :: " << firstNode << endl;
q.push({nextNode,{nextValue, firstNode}});
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin >> N >> M;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++){
int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;
arr[a].push_back({b, c});
arr[b].push_back({a, c});
}
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= N; j++){
dist[j] = 1e9;
}
dijk(i);
}
// cout << "======" << endl;
// for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
// cout << dist[i] << ' ';
// }
// cout << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++){
if(i == j) cout << "- ";
else cout << answer[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
}
'PS > 백준 문제 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 17298번] 오큰수 (C++) (0) | 2025.04.22 |
|---|---|
| [백준 1949번] 우수 마을 (C++) (0) | 2025.04.22 |
| [백준 1082번] 방 번호 (C++) (0) | 2025.04.09 |
| [백준 1033번] 칵테일 (C++) (0) | 2025.03.31 |
| [백준 2138번] 전구와 스위치(C++) (0) | 2025.03.22 |



