728x90
기본적인 사용법:
선언 - map<int, int> test;
삽입 - test.insert(make_pair(key, value))
제거 - test.erase(key)
ex)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<int, int> test;
test.insert(make_pair(1, 10));
test.insert(make_pair(2, 9));
test.insert(make_pair(3, 8));
test.insert(make_pair(4, 7));
test.insert(make_pair(5, 6));
cout << test[1] << endl;
cout << test[2] << endl;
cout << test[3] << endl;
cout << test[4] << endl;
cout << test[5] << endl;
}
그렇다면 map의 담겨있는 것을 반복문으로 보고싶다면 어떻게 해야할까?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<int, int> test;
test.insert(make_pair(1, 10));
test.insert(make_pair(2, 9));
test.insert(make_pair(3, 8));
test.insert(make_pair(4, 7));
test.insert(make_pair(5, 6));
for (auto a : test) {
cout << a.first << " " << a.second << endl;
}
}
auto a : test 방식은 Container 형식이면 모두 가능하다. 벡터, 맵이 대표적이다.
그리고 보다시피 맵은 key가 오름차순으로 정렬되어있다. 그러나 가끔은 value의 어떤 기준으로 정렬해야할 필요가 있다. 이때, 맵 오리지널을 정렬할 순 없고 벡터에 옮긴 후 정렬해야한다.
vector<pair<int,int>> vec( test.begin(), test.end() );그리고 벡터를 정렬하는 sort함수를 사용해 원하는 대로 정렬하면 된다. 여기선 value를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬해보겠다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool comp(pair<int, int>& a, pair<int, int>& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
}
int main() {
map<int, int> test;
test.insert(make_pair(1, 10));
test.insert(make_pair(2, 9));
test.insert(make_pair(3, 8));
test.insert(make_pair(4, 7));
test.insert(make_pair(5, 6));
vector<pair<int, int>> vec(test.begin(), test.end());
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), comp);
for (auto a : vec)
cout << a.first << " " << a.second << endl;
}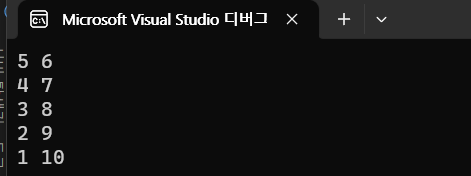
value 형식으로 정렬되어있다.
'개발 > C,C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| vector<int> 보다 vector<bool> 이 느리다? (0) | 2024.08.08 |
|---|---|
| C++ vector 초기화 방법 (0) | 2023.10.29 |
| 시퀀스 컨테이너 - list (0) | 2023.03.26 |
| C++ 문자열 자르기 split / 문자열 <-> 정수 형 변환 (0) | 2023.03.25 |
| C++ 연관 컨테이너 set, mutiset (0) | 2023.03.22 |
